This guide focuses on the most frequently used Philippines‑specific modules. Each section explains how to navigate to the relevant menu, set conditions and parameters, and generate the required documents.
Introduction
In the Philippines, companies that use accounting software must register their systems with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR) under the Computerized Accounting System (CAS) requirements. Revenue Memorandum Circular No. 5‑2021 simplified the registration process but also clarified the forms and ledgers that must be produced for compliance. multibook offers a suite of modules to meet these requirements: it can generate compliant invoices and official receipts, produce journal lists and general ledgers for loose‑leaf books, create withholding tax certificates, and output BIR submission files. Looking ahead, multibook will also support the upcoming Electronic Invoicing/Receipting System (EIS) expected to roll out from 2025.
Overview of CAS Compliance Functions
The table below summarises the principal requirements for CAS registration and the corresponding multibook modules. Later sections of this guide explain how to operate the highlighted functions.
|
Requirement type |
Key requirements |
Supporting multibook modules |
|
PH CAS requirements |
Display mandatory information on invoices and receipts |
ACPH110 Invoice, ACPH120 Official Receipt |
|
Accounting books |
Print journal lists, general ledgers, trial balances and other ledgers |
ACPH210 BIR Loose‑leaf Book of Accounts, ACGL420 Sales/Purchase Journal List, ACGL620 Financial Statements |
|
Withholding tax |
Issue certificates for final and expanded withholding tax |
ACPH250 BIR Form 2307, ACPH270 BIR Form 2306 |
|
Tax filings |
Generate interface files for withholding tax and VAT returns |
ACPH220 BIR Interface File (1601EQ), ACPH230 BIR Interface File (1604E), ACPH240 BIR Interface File (2550Q) |
|
Local practices |
Print cheques, support multiple currencies |
ACPH260 Check Printing (PH), ACC3620 Financial Statements (3rd) |
The remainder of this guide provides step‑by‑step instructions for Invoice, Official Receipt, BIR Loose‑leaf Book of Accounts, and BIR Form 2306 modules.
ACPH110 Invoice – Generating Invoices
Overview
The ACPH110 Invoice module produces invoices based on accounting entries. It automatically populates the seller’s name, address and TIN, assigns invoice and series numbers, and breaks down sales by VAT type. Invoices can be printed as PDFs or exported to Excel.
Navigating to the menu
From the accounting menu, select Country Specific Function → Philippines and choose ACPH110 Invoice. The red box in the screenshot below indicates where to find this menu item.

Operation steps
- Enter search conditions – The company code defaults to the user’s company. You may leave optional fields blank or specify ranges to narrow your search. The main parameters are:
- Doc No./Invoice No./Posting Date/Doc Date/Doc Type – Each accepts a range to filter the documents.
- Biz Partner – Restrict results to a particular business partner if required.
- Currency – Specify a currency if you only want documents in that currency. Leaving this blank searches all currencies.
- Cleared – Choose Open to see only unreconciled entries or All to include cleared documents.
- Number of Copies – How many copies to print (mandatory).
- Title – The heading to display on the invoice (mandatory).
- VATable Tax/VAT‑Exempt Tax/Zero Rated Tax – Enter a tax code to output only items of that VAT category (optional).
- Invoice Date – Select whether the invoice date uses the posting date or document date (mandatory).
The search form looks like this:

- Review field definitions – Before running the search, you can consult the help table that explains each parameter, whether it is required and any notes. In particular, the company code, number of copies, title and invoice date are mandatory.

- Export invoices – After performing the search, tick the boxes next to the documents you wish to output and press Export. Choose either PDF or Excel format. You can also select:
- Print “REPRINT” – Adds a “REPRINT” watermark if the invoice is being re‑issued.
- Print “THIS DOCUMENT IS NOT VALID FOR CLAIM OF INPUT TAX” – Adds a disclaimer if the invoice should not be used for input VAT claims, such as a supplementary invoice.
For multiple invoices, the system will bundle the files into a Zip archive. A sample export screen is shown below:

Additional notes
- The seller’s details printed on the invoice come from the company master (MACM110). Invoice numbers consist of the document type code, numbering unit and an automatically assigned sequence. You can configure the numbering ranges in the administration menu.
- When you specify a tax code in the VATable/VAT‑Exempt/Zero Rated Tax fields, mixed transactions are split so that only items in the chosen tax category appear.
- Excel outputs follow a fixed template and are not ideal for editing. For modifications, consider exporting to PDF.
ACPH120 Official Receipt – Issuing Receipts
Overview
ACPH120 Official Receipt issues receipts for incoming payments. The interface is almost the same as for invoices, except that receipt numbers and payment dates are used instead. You can also customise the title and show amounts by tax category.
Navigating to the menu
Select Country Specific Function → Philippines and then ACPH120 Official Receipt. The menu position is highlighted below.

Operation steps
- Set search parameters – Enter the company code, document numbers, date ranges, business partner, and currency as needed. As with invoices, the number of copies and title fields are mandatory. The search screen appears as follows:

- Review field definitions – The meaning of each parameter is the same as in the invoice module, but note that receipts are based on incoming payments. Therefore, the document type and date fields correspond to payments rather than sales.

- Export receipts – After searching, select the relevant entries and press Export. As with invoices, you can print a “REPRINT” or “NOT VALID FOR CLAIM OF INPUT TAX” notice if required. The export screen looks like this:

Additional notes
- Receipt numbers follow the same sequencing rules as invoices. Check that numbering units are properly configured to avoid gaps.
- When exporting to Excel, each receipt is placed in its own sheet. If many receipts are generated, they will be downloaded as a Zip file.
ACPH210 BIR Loose‑leaf Book of Accounts – Journal and Ledger Outputs
Overview
The BIR requires companies using electronic systems to print and bind journal lists and general ledgers. ACPH210 BIR Loose‑leaf Book of Accounts facilitates this by producing Excel files containing the journal details or general ledger balances for a specified period. You select the company, fiscal year and month, ledger category and output type, and the system generates the appropriate book.
Navigating to the menu
In the accounting menu, choose Country Specific Function → Philippines and click ACPH210 BIR Loose‑leaf Book of Accounts. It is highlighted in the screenshot below:

Operation steps
- Specify output parameters – The required fields are:
- Company – The company code to output.
- Year/Month – The accounting period.
- Ledger – Choose Normal, Ledger 1 or Ledger 2.
- Output – Select Journal List or General Ledger.
Enter these values and press Execute. The search screen includes a help table explaining each item:

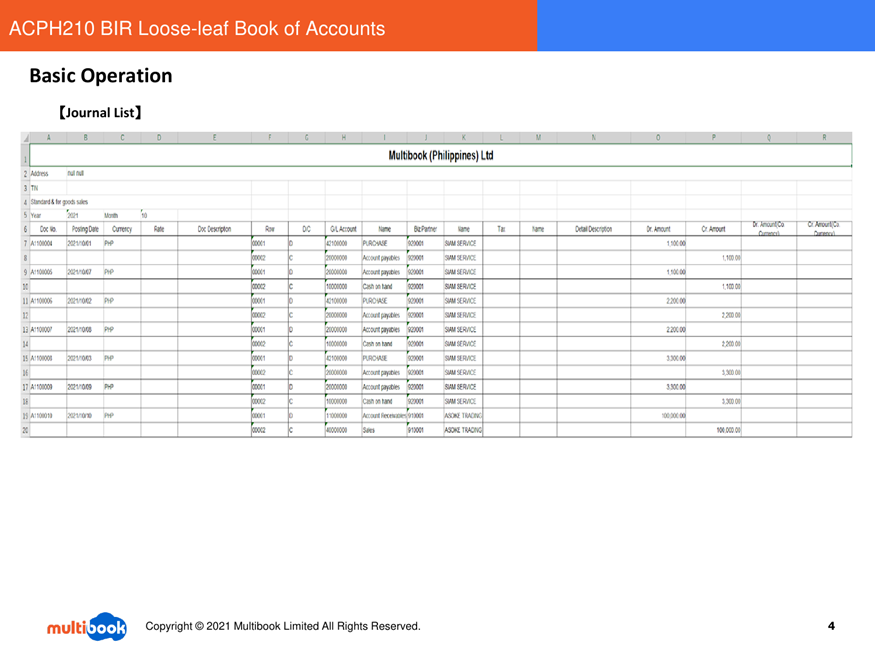
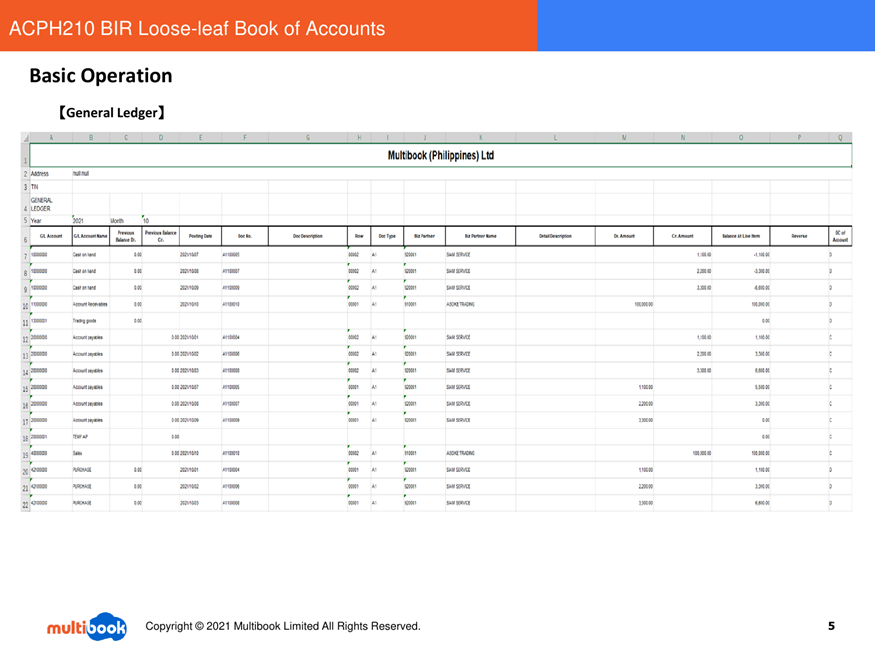
- View outputs – The system exports an Excel file containing the selected book. The journal list lists each transaction line with date, document number, debit and credit accounts, amount and business partner. The general ledger summarises balances by account. Sample outputs are shown below:
- Journal List sample:
- General Ledger sample:
Additional notes
- These Excel outputs are intended to be printed and bound for submission to the BIR. Avoid altering the layout, as changes could lead to comments during the approval process.
- Companies may choose to use Ledger 1 or Ledger 2 for specific purposes. If these categories are not in use, simply select Normal.
ACPH270 BIR Form 2306 – Certificates of Final Withholding Tax
Overview
ACPH270 BIR Form 2306 issues certificates for Final Withholding Tax on payments to non‑resident payees. Even when transactions are in a foreign currency, the system converts them to Philippine pesos (PHP). The module creates one certificate per document; when multiple documents are selected, separate PDF files are produced and zipped together. Each ATC code (withholding tax code) must have an associated withholding tax account defined in advance.
Understanding Final Withholding Tax
The following diagram illustrates how final withholding tax works: the payer deducts tax from the payment and remits it to the authorities, while the payee receives the net amount along with the certificate.

Key points

- Amounts are converted to PHP – Even if the transaction currency differs, the system calculates the amounts in PHP. It ignores the company currency when the company currency is PHP.
- One certificate per document – Multiple selections result in multiple PDFs packed into a single zip file.
- Accounts by ATC code – Each ATC code must be linked to a withholding tax account (GL account type “WHD Account”).
- Tax base stored in D.spare num1 – The underlying amount used for withholding tax is stored in this additional field on the journal line.
Operation steps
- Enter search conditions – In the ACPH270 BIR Form 2306 screen, specify the company and the period (year/month range). Then choose the withholding tax account, optionally filter by business partner or individual category, and set the exchange rate type. The search form appears as follows:

A help table explains each field:

- Select documents and export – After searching, tick the entries you want and click Export. If multiple documents are selected, you’ll receive a zipped set of PDFs.

- Review the certificates – The output follows the BIR Form 2306 layout, automatically filling in the period, payee details, amounts, tax rate and ATC code. A sample section is shown below:

Additional notes
- If the transaction currency is not PHP, the system uses the exchange rate type you specify to convert amounts. Make sure exchange rates are maintained in the master data; otherwise, an error will occur.
- The tax base for withholding must be recorded in the spare num1 field of each journal line. If this value is missing, the certificate shows zero.
- Form 2306 documents are used by payers (buyers). Vendors receiving the certificates need their own process to manage them.
Preparing for the Electronic Invoicing/Receipting System (EIS)
From 14 March 2025, the BIR will introduce the Electronic Invoicing/Receipting System (EIS). Selected taxpayers must be ready for live operation by 14 March 2026, with other companies to follow. The aim of EIS is to increase tax transparency, prevent fraud and streamline audits.
EIS overview

multibook’s solution
multibook plans to automate the flow from invoice registration to submission to the EIS API, and then retrieve the approval status from the BIR. By integrating invoice e‑mail delivery and withholding tax certificate output, the solution will simplify Filipino billing processes.

Release schedule
Development and testing for EIS support are scheduled from July to November 2025, with a public release planned for November. The timeline is illustrated below:

Other related functions
- ACPH220/ACPH230/ACPH240 BIR Interface Files – These modules generate XML or CSV files for withholding tax and VAT returns. You select the relevant journal entries, and the system outputs them in a format accepted by the BIR.
- ACPH250 BIR Form 2307 – Issues certificates for expanded withholding tax. Unlike Form 2306, it is the payee’s version of the certificate.
- ACGL420 Sales/Purchase Journal List – Produces lists of sales and purchase entries used for VAT returns.
- ACPH260 Check Printing (PH) – Prints cheques using local bank formats and automatically converts amounts into words.
Operational notes
- When specifying company codes and periods in each module, double‑check the ranges to avoid producing reports with incorrect data. Pay special attention when generating tax forms: ensure the correct accounts and exchange rate types are defined beforehand.
- Selecting multiple entries in a list will result in a Zip file download. Unzip the file to access the individual reports.
- PDF exports have fixed layouts and are not designed for editing. If you need to adjust the layout, export to Excel first and then make changes.
Conclusion
This guide has provided an overview of key multibook functions that meet the Philippine CAS requirements. We explained how to generate invoices and receipts, output journal and ledger books, and create final withholding tax certificates. We also previewed the forthcoming EIS support. By following the steps outlined here, companies can ensure compliance with BIR regulations and streamline their accounting operations in the Philippines. As always, review your company’s specific policies and tax requirements when configuring and using these functions.
